基于Paillier算法的匿名电子投票流程实现(Go实现)
实验名称:基于Paillier 算法的匿名电子投票流程实现
实验原理:
Paillier加密算法是佩利尔在1999年发明的概率公钥加密算法。该算法基于复合剩余类的困难问题,是一种满足加法同态性质的加密算法。该算法已经被广泛应用于加密信号处理以及第三方数据处理领域。Paillier算法如下图所示。

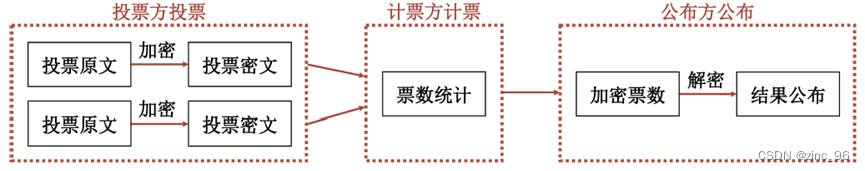
在电子投票系统中,由于统计票数是使用加法累加票数进行统计的,因此具有加法同态性质的Paillier算法可被应用于实现匿名的电子投票系统,以保护投票人的投票信息。电子投票系统架构如下图所示。
实验环境:Windows 11 + Go 1.20.4
实验步骤:
1.配置实验环境
1.1配置Go语言环境:
1.1.1下载和安装Go语言SDK,下载地址:https://golang.org/dl/
下载go1.20.4.windows-amd64.msi文件后,点击安装。
1.1.2配置系统环境变量
新增 GOROOT,即 GO 语言安装目录
在系统变量自带的 Path 下添加路径%GOROOT%\bin
创建工程文件夹,为了方便识别,需要在文件夹中创建bin、pkg、src三个文件夹
新增 GOPATH,即刚才创建的GO 的工程目录
在系统变量自带的Path下添加路径%GOPATH%
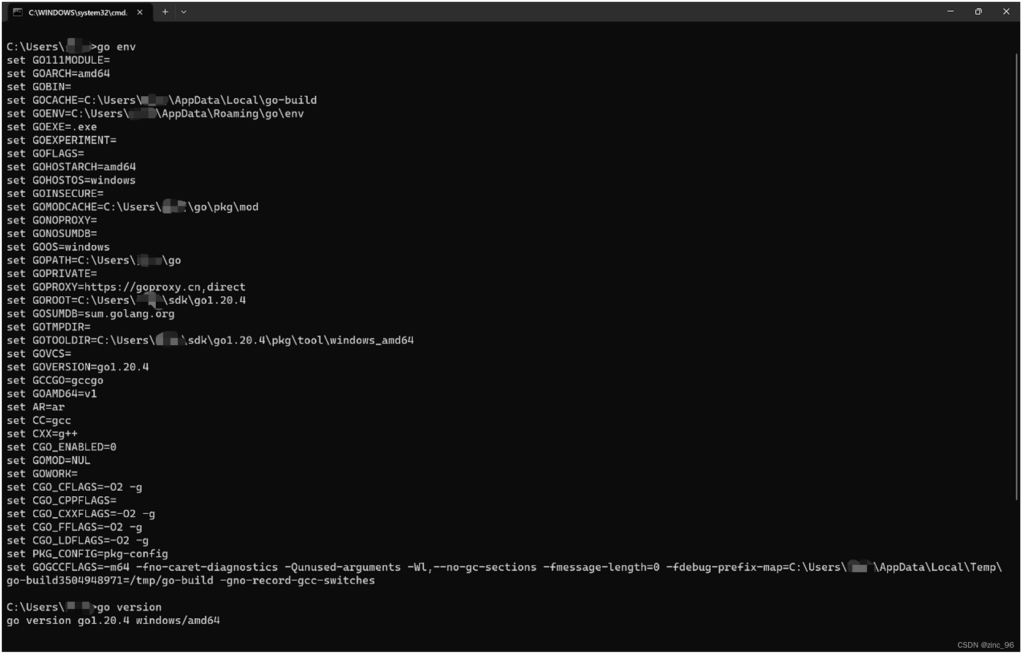
打开命令行工具,输入命令go env和go version,显示类似下图说明配置成功
2.创建Go语言代码文件,编写Paillier加密程序,验证Paillier算法具有加法同态性:
package main
import (
"crypto/rand"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/big"
)
var one = big.NewInt(1)
// ErrMessageTooLong 当所需加密信息长度大于公钥长度时,报错。
var ErrMessageTooLong = errors.New("信息过长!请调整公钥长度!")
// GenerateKey 生成指定位数的公私钥。
func GenerateKey(random io.Reader, bits int) (*PrivateKey, error) {
// 生成素数p
var p *big.Int
var errChan = make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
var err error
p, err = rand.Prime(random, bits/2)
errChan <- err
}()
// 生成素数q
q, err := rand.Prime(random, bits/2)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 等待素数p生成完成
if err := <-errChan; err != nil {
return nil, err
}
n := new(big.Int).Mul(p, q)
pp := new(big.Int).Mul(p, p)
qq := new(big.Int).Mul(q, q)
return &PrivateKey{
PublicKey: PublicKey{
N: n,
NSquared: new(big.Int).Mul(n, n),
G: new(big.Int).Add(n, one), // g = n + 1
},
p: p,
pp: pp,
pminusone: new(big.Int).Sub(p, one),
q: q,
qq: qq,
qminusone: new(big.Int).Sub(q, one),
}, nil
}
// PrivateKey 私钥
type PrivateKey struct {
PublicKey
p *big.Int
pp *big.Int
pminusone *big.Int
q *big.Int
qq *big.Int
qminusone *big.Int
Lambda *big.Int
}
// PublicKey 公钥
type PublicKey struct {
N *big.Int
G *big.Int
NSquared *big.Int
}
// L L(x)=(x-1)/n
func L(x, n *big.Int) *big.Int {
return new(big.Int).Div(new(big.Int).Sub(x, one), n)
}
// Encrypt 加密。
func Encrypt(pubKey *PublicKey, plainText []byte) ([]byte, *big.Int, error) {
r, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, pubKey.N)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
m := new(big.Int).SetBytes(plainText)
if pubKey.N.Cmp(m) < 1 { // N < m
return nil, nil, ErrMessageTooLong
}
// c = g^m * r^n mod n^2 = [(m*n+1) mod n^2] * r^n mod n^2
c := new(big.Int).Mod(
new(big.Int).Mul(
new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Add(one, new(big.Int).Mul(m, pubKey.N)), pubKey.NSquared),
new(big.Int).Exp(r, pubKey.N, pubKey.NSquared),
),
pubKey.NSquared,
)
return c.Bytes(), r, nil
}
// Decrypt 解密。
func Decrypt(privKey *PrivateKey, cipherText []byte) ([]byte, error) {
c := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipherText)
if privKey.NSquared.Cmp(c) < 1 {
return nil, ErrMessageTooLong
}
mu := new(big.Int).ModInverse(privKey.Lambda, privKey.N)
m := new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Mul(L(new(big.Int).Exp(c, privKey.Lambda, privKey.NSquared), privKey.N), mu), privKey.N)
return m.Bytes(), nil
}
// AddCipher 将两个密文相乘,以达到明文相加的目的。
func AddCipher(pubKey *PublicKey, cipher1, cipher2 []byte) []byte {
x := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipher1)
y := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipher2)
// x * y mod n^2
return new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Mul(x, y), pubKey.NSquared).Bytes()
}
func main() {
// 生成一个4096位私钥
privKey, err := GenerateKey(rand.Reader, 4096)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
privKey.Lambda = new(big.Int).Mul(privKey.pminusone, privKey.qminusone)
// 加密明文1
fmt.Print("请输入第一个明文:")
var Plaintext1 big.Int
fmt.Scan(&Plaintext1)
Cipher1, _, err := Encrypt(&privKey.PublicKey, Plaintext1.Bytes())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// 加密明文2
fmt.Print("请输入第二个明文:")
var plaintext2 big.Int
fmt.Scan(&plaintext2)
Cipher2, _, err := Encrypt(&privKey.PublicKey, plaintext2.Bytes())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("对第一个明文加密后得到密文:", new(big.Int).SetBytes(Cipher1))
fmt.Println("对第二个明文加密后得到密文:", new(big.Int).SetBytes(Cipher2))
// 将明文1与明文2相加。
EncryptedPlusCipher1Cipher2 := AddCipher(&privKey.PublicKey, Cipher1, Cipher2)
fmt.Println("两密文相乘得到:", new(big.Int).SetBytes(EncryptedPlusCipher1Cipher2))
DecyptedPlusCipher1Cipher2, err := Decrypt(privKey, EncryptedPlusCipher1Cipher2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("密文相乘后解密得到的明文为:", new(big.Int).SetBytes(DecyptedPlusCipher1Cipher2))
}3.运行Paillier加密程序,结果如下图所示,说明Paillier算法具有加法同态性。
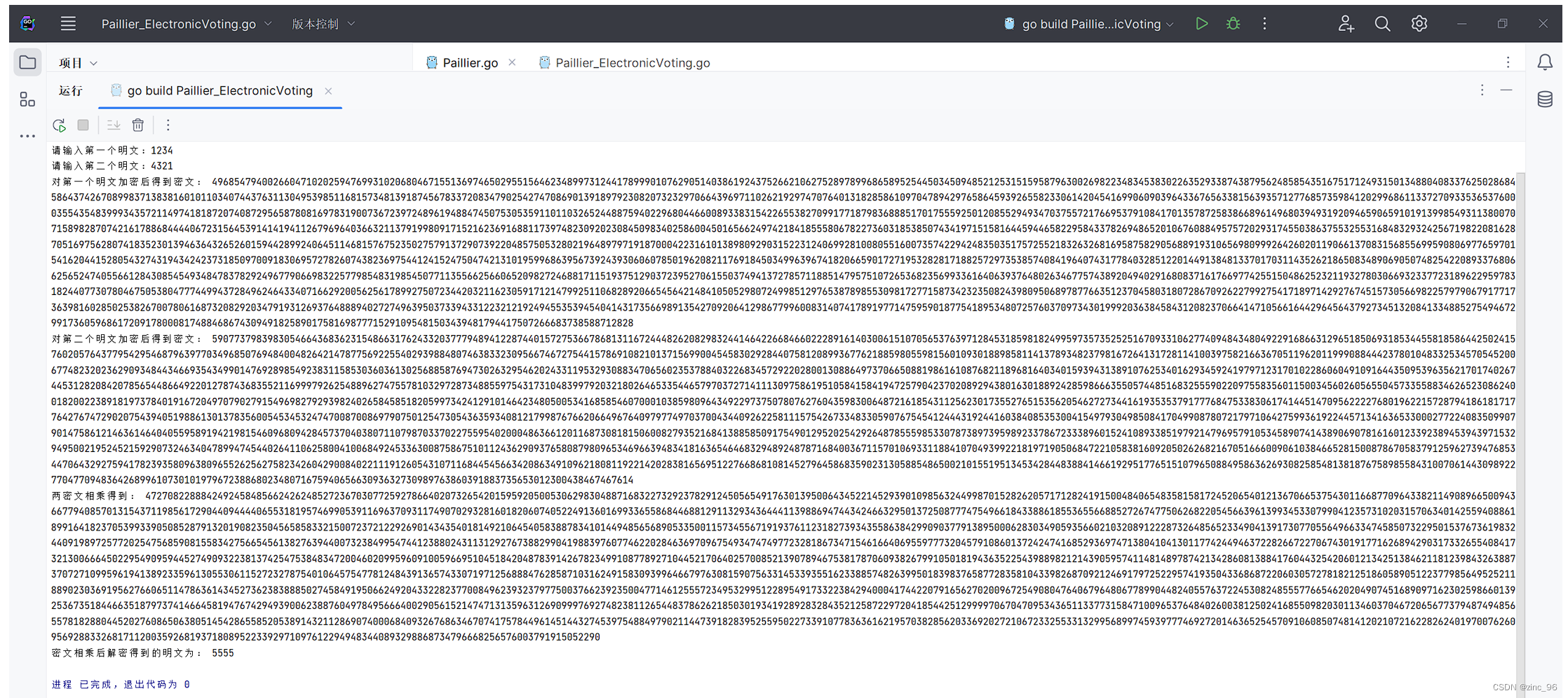
4.创建Go语言代码文件,编写基于Paillier的电子投票系统:
package main
import (
"crypto/rand"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/big"
)
var one = big.NewInt(1)
// ErrMessageTooLong 当所需加密信息长度大于公钥长度时,报错。
var ErrMessageTooLong = errors.New("信息过长!请调整公钥长度!")
// GenerateKey 生成指定位数的公私钥。
func GenerateKey(random io.Reader, bits int) (*PrivateKey, error) {
// 生成素数p
var p *big.Int
var errChan = make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
var err error
p, err = rand.Prime(random, bits/2)
errChan <- err
}()
// 生成素数q
q, err := rand.Prime(random, bits/2)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 等待素数p生成完成
if err := <-errChan; err != nil {
return nil, err
}
n := new(big.Int).Mul(p, q)
pp := new(big.Int).Mul(p, p)
qq := new(big.Int).Mul(q, q)
return &PrivateKey{
PublicKey: PublicKey{
N: n,
NSquared: new(big.Int).Mul(n, n),
G: new(big.Int).Add(n, one), // g = n + 1
},
p: p,
pp: pp,
pminusone: new(big.Int).Sub(p, one),
q: q,
qq: qq,
qminusone: new(big.Int).Sub(q, one),
}, nil
}
// PrivateKey 私钥
type PrivateKey struct {
PublicKey
p *big.Int
pp *big.Int
pminusone *big.Int
q *big.Int
qq *big.Int
qminusone *big.Int
Lambda *big.Int
}
// PublicKey 公钥
type PublicKey struct {
N *big.Int
G *big.Int
NSquared *big.Int
}
// L L(x)=(x-1)/n
func L(x, n *big.Int) *big.Int {
return new(big.Int).Div(new(big.Int).Sub(x, one), n)
}
// Encrypt 加密。
func Encrypt(pubKey *PublicKey, plainText []byte) ([]byte, *big.Int, error) {
r, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, pubKey.N)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
m := new(big.Int).SetBytes(plainText)
if pubKey.N.Cmp(m) < 1 { // N < m
return nil, nil, ErrMessageTooLong
}
// c = g^m * r^n mod n^2 = [(m*n+1) mod n^2] * r^n mod n^2
c := new(big.Int).Mod(
new(big.Int).Mul(
new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Add(one, new(big.Int).Mul(m, pubKey.N)), pubKey.NSquared),
new(big.Int).Exp(r, pubKey.N, pubKey.NSquared),
),
pubKey.NSquared,
)
return c.Bytes(), r, nil
}
// Decrypt 解密。
func Decrypt(privKey *PrivateKey, cipherText []byte) ([]byte, error) {
c := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipherText)
if privKey.NSquared.Cmp(c) < 1 {
return nil, ErrMessageTooLong
}
mu := new(big.Int).ModInverse(privKey.Lambda, privKey.N)
m := new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Mul(L(new(big.Int).Exp(c, privKey.Lambda, privKey.NSquared), privKey.N), mu), privKey.N)
return m.Bytes(), nil
}
// AddCipher 将两个密文相乘,以达到明文相加的目的。
func AddCipher(pubKey *PublicKey, cipher1, cipher2 []byte) []byte {
x := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipher1)
y := new(big.Int).SetBytes(cipher2)
// x * y mod n^2
return new(big.Int).Mod(new(big.Int).Mul(x, y), pubKey.NSquared).Bytes()
}
func SendtoTeller(evts *[][]byte, evt [][]byte, canum int, pubKey *PublicKey) {
for i := 0; i < canum; i++ {
(*evts)[i] = AddCipher(pubKey, (*evts)[i], evt[i])
}
}
func SendtoSpokesman(evts *[][]byte, canum int, privKey *PrivateKey) {
var err error
var Winner = 0
for i := 0; i < canum; i++ {
(*evts)[i], err = Decrypt(privKey, (*evts)[i])
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("第", i+1, "位候选人获得了", new(big.Int).SetBytes((*evts)[i]), "张选票;")
if new(big.Int).SetBytes((*evts)[Winner]).Cmp(new(big.Int).SetBytes((*evts)[i])) < 1 {
Winner = i
}
}
fmt.Println("最终第", Winner+1, "位候选人获得的选票最多,为", new(big.Int).SetBytes((*evts)[Winner]), "张")
return
}
func main() {
// 生成一个4096位私钥
privKey, err := GenerateKey(rand.Reader, 4096)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
privKey.Lambda = new(big.Int).Mul(privKey.pminusone, privKey.qminusone)
// 程序开始运行提示
fmt.Println("**********此程序模拟了基于Paillier算法的匿名电子投票的流程**********")
fmt.Println("首先每位投票者为候选人投票并将结果加密发送给计票人。每人只有1张选票,\n选票上被投票的候选者得到1张选票,其他候选者得到0张选票;")
fmt.Println("然后计票人将所有选票上对应候选人的加密的投票结果相乘,并将加密的统计\n结果发送给公布人;")
fmt.Println("最后公布人对统计的票数进行解密并公布。")
fmt.Println("********************************************************************")
fmt.Print("请设置候选者人数:")
var CandidatesNum int
fmt.Scan(&CandidatesNum)
if CandidatesNum <= 0 {
fmt.Println("候选者人数至少为1")
return
}
EncryptedVotes := make([][]byte, CandidatesNum)
for i := 0; i < CandidatesNum; i++ {
EncryptedVotes[i], _, err = Encrypt(&privKey.PublicKey, big.NewInt(int64(0)).Bytes())
}
fmt.Print("请设置投票者人数:")
var VotersNum int
fmt.Scan(&VotersNum)
if VotersNum <= 0 {
fmt.Println("投票者人数至少为1")
return
}
// 投票提示
for i := 0; i < VotersNum; i++ {
fmt.Println("-----请第", i+1, "名投票者为候选者投票-----")
Vote := make([]int, CandidatesNum)
var flag bool
for j := 0; j < CandidatesNum; j++ {
fmt.Print("请为第", j+1, "名候选者投票:")
fmt.Scan(&Vote[j])
if Vote[j] == 1 {
if flag {
fmt.Println("非法投票!每位投票者只有1张选票!")
return
}
flag = true
}
}
// 将加密的投票结果发给计票人
EncryptedVote := make([][]byte, CandidatesNum)
for i := 0; i < CandidatesNum; i++ {
EncryptedVote[i], _, err = Encrypt(&privKey.PublicKey, big.NewInt(int64(Vote[i])).Bytes())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
}
fmt.Println("对该投票结果进行加密并发送给计票人")
fmt.Println("计票人对此投票结果进行计票")
SendtoTeller(&EncryptedVotes, EncryptedVote, CandidatesNum, &privKey.PublicKey)
}
fmt.Println("-----计票人计票完成并将加密后的投票结果发给公布人-----")
fmt.Println("加密后的投票结果为:")
for i := 0; i < CandidatesNum; i++ {
fmt.Println("第", i+1, "位候选人获得的选票票数的加密结果为", new(big.Int).SetBytes(EncryptedVotes[i]))
}
fmt.Println("-----公布人解密计票结果并公布最终的投票结果-----")
SendtoSpokesman(&EncryptedVotes, CandidatesNum, privKey)
}5.运行电子投票系统,结果如下图所示: